Lung capacity is a familiar term for those living with chronic pulmonary conditions, but it is also important as a general health assessor. Increasing lung capacity can be an important goal for those looking to improve their respiratory health. Studies have shown evidence that short and long-term practicers of meditation have a significantly higher lung capacity than non-meditators.
Total lung capacity, or TLC, refers to the maximum amount of air that your lungs can hold. As we get older, our lung capacity decreases. This means it becomes harder to deliver the same amount of oxygen to our body and cells as previously, and our heart has to pick up the work of pumping oxygen around the body. The heart working overtime can lead to heart complications, so it’s important we do everything we can to strengthen our lung capacity and maximize the flow of oxygen through our respiratory system.
In this article, we will take a look at what is meditation, the benefits for lung capacity, and how you can utilize meditation to see positive results.
What is meditation?
Meditation is an ancient practice that is believed to have originated in India several thousand years ago but has evolved into many different forms, religions, health exercises and styles of practice since. Meditation still plays a central role in many religious traditions and rituals, in addition to helping individuals to manage stress, health conditions and improve overall well-being. In 1979, the Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program was founded in the United States, which used meditative techniques in the treatment plans for patients with chronic diseases and took a health-based focus.
Most meditations begin by sitting in a quiet place, closing the eyes, calming the mind, and focusing on the breath. Meditation can be 5 minutes with your eyes closed or hours of peaceful mind exercises. The main takeaway is that meditation may look like one thing for one person and entirely different to the next!

What benefits does meditation have for lung health?

To understand the impact of meditation on improving lung health, it’s important to look at the physical health benefits holistically. When our mind is under stress, either from personal or health-based reasons, our body takes the brunt of the physical impact. For example, too much cortisol can increase blood sugar levels, suppress the immune system, and constrict blood vessels making it difficult to pump oxygen effectively through the body.
When we relax the mind and body by practicing meditation and other breathing exercises, we can reduce the discomfort of inflammation and aid the flow of oxygen to our cells. Meditation involves observing correct breathing patterns and training your body effectively utilize your breathing patterns. Taking control of your breath can help improve lung capacity and open your airways.
How do I get started?
Learning to meditate to improve breathing is like any other skill. All it takes is a little practice and you’ll be able to master it in no time.
1. Simply choose a time and place that works for you.
To see the best results, it’s important to repeat the process a number of times. The best way to create a habit is to choose a time and place that works for you and that you can incorporate into your routine. Maybe it is just taking a few minutes lying in bed after you wake up in the morning, or as you wait for your coffee machine to finish at the breakfast table. It could be before you go to sleep at night, or on your train home from work! But make sure it is somewhere where you can feel comfortable and will be minimally distracted.
2. Make sure you are sitting comfortably.
Sit with your legs and arms uncrossed, feet flat on the floor, and hands resting on your lap or by your side. Make sure your back is straight, but not too tense. A small cushion or rolled-up towel can help keep your back straight if you need it.
3. Begin your breathing exercises.
There are a few different breathing exercises you can choose depending on your focus. In the next section, we’ll outline the best exercises for improving your lung capacity.

What exercises help improve lung capacity?
There are a number of exercises you can integrate into your daily routine and lifestyle with minimal effort.
Diaphragmatic Breathing
Used by athletes, opera singers, musicians, and many more, diaphragm exercises help retrain this muscle in the respiratory system to work more efficiently.
1. While sitting down, close your eyes and relax your shoulders.
2. Put one hand on your chest and place the other hand on your stomach.
3. Deep breathe in through your nose for 5 seconds. Tip: You’re breathing correctly if you can feel your stomach move more than your chest.
4. Purse your lips and breath out slowly through your mouth for 8 seconds, pressing lightly on your stomach
Repeat 4-5 times or as you are able.
Box Breathing (or ‘4-count Breathing’)
A popular method with the US Navy, Box Breathing is used for pain management and calming the nervous system quickly.
1. Sitting upright, slowly exhale through your mouth, getting all the oxygen out of your lungs.
2. Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose to the count of four. Feel the air fill your lungs, one section at a time until your lungs are completely full and the air moves into your abdomen.
3. Hold your breath for a count of 4.
4. Exhale through your mouth for the same slow count of four, expelling the air from your lungs and abdomen.
OPEP Device Exercises
This method is often recommended for those diagnosed with COPD and other respiratory illnesses in daily therapy.
1. Sit upright, with your back straight against the chair and feet flat against the floor.
2. Take a deep breath in, focusing on your breath as it fills up your lungs.
3. Place the OPEP device in between the lips and exhale through the mouth for at least 5 seconds, until you can raise the metal ball in the air.
4. Focus on feeling the vibrations on your lips.
Repeat for 5-10 minutes.
Why use an OPEP device?
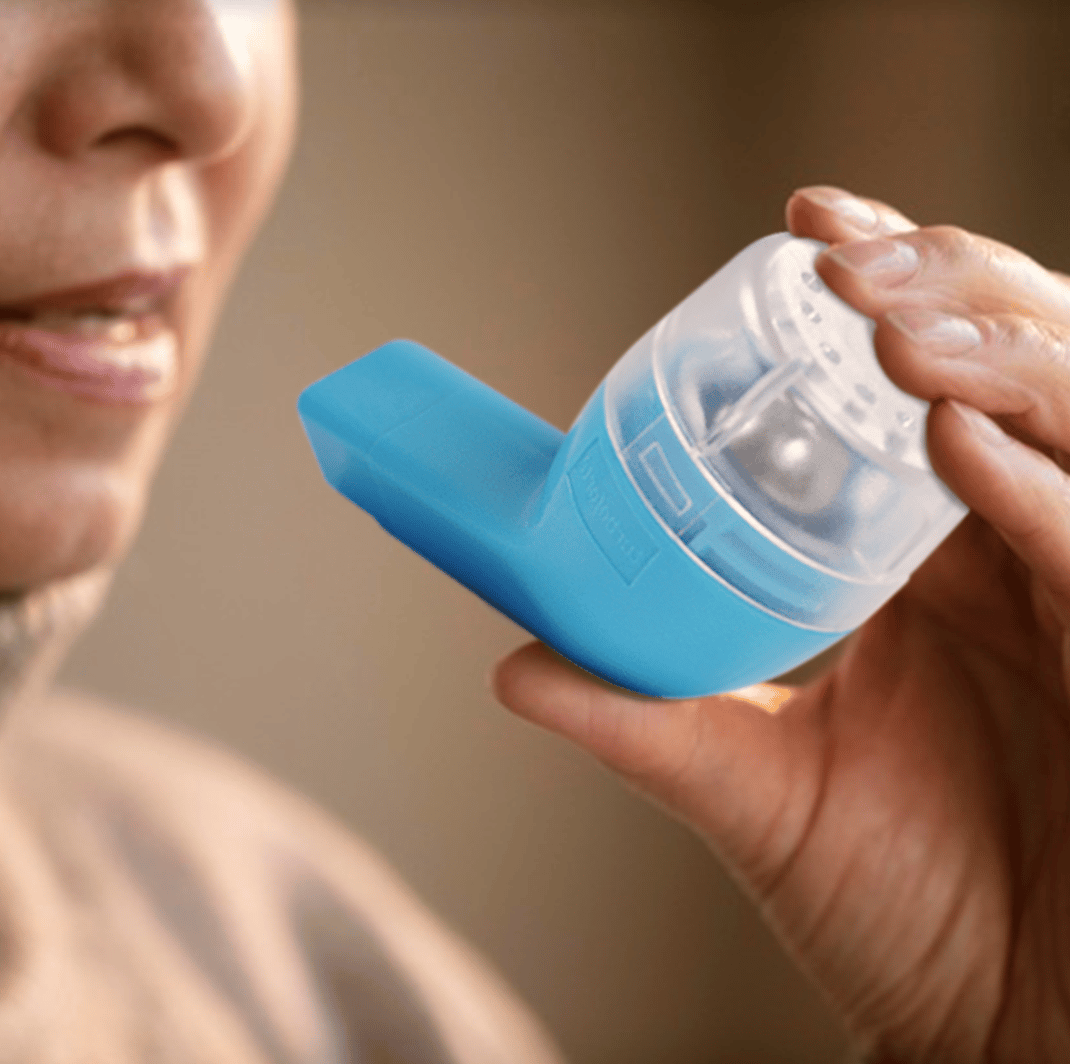

Turboforte is easy to use, non-invasive, and medically approved. Read about how Turboforte has helped thousands in our customer testimonials here or purchase one for yourself today.
While Turboforte is a drug-free, all-natural way to help and can be used in conjunction with your usual treatment regime, always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. Never disregard the advice of a medical professional, or delay in seeking it because of something you have read that contradicts your doctor’s personal advice.